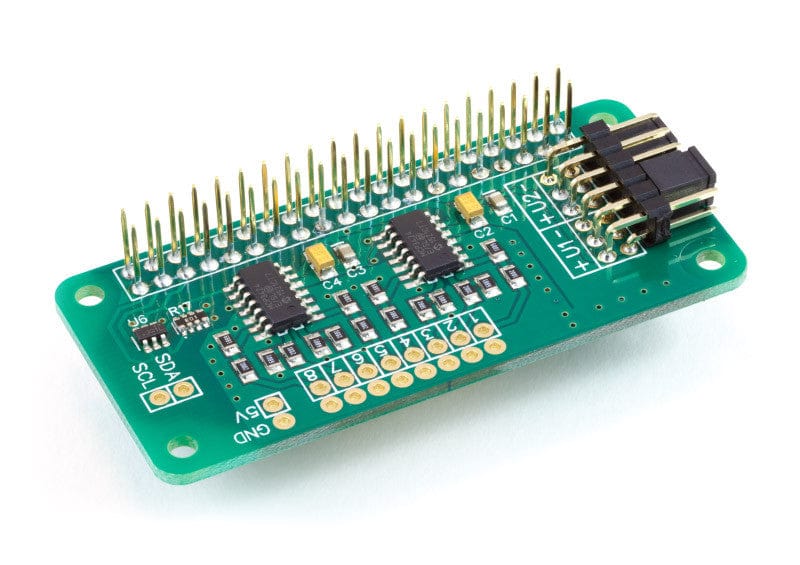
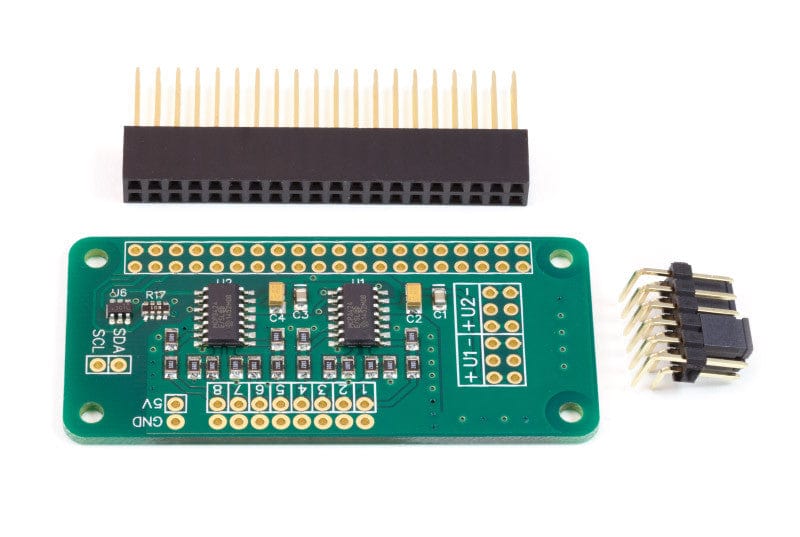
Der ADC Pi Zero ist ein 8-Kanal 17-Bit Analog-Digital-Wandler, der für den Raspberry Pi Zero entwickelt wurde. Der ADC Pi Zero basiert auf zwei Microchip MCP3424 A/D-Wandlern mit jeweils 4 analogen Eingängen. Der MCP3424 ist ein Delta-Sigma-A/D-Wandler mit rauscharmen Differenzeingängen.
Wir haben den ADC Pi Zero so konzipiert, dass er als Single-Ended-A/D-Wandler mit der internen 2,048-V-Referenzspannung arbeitet, wobei die -V-Pins mit Masse verbunden sind. Ein Spannungsteiler auf der ADC Pi Zero Platine bringt den Eingangsspannungsbereich auf einen viel nützlicheren Wert von 0 - 5,06V. In dieser Konfiguration beträgt die Abtastgröße 17 Bit für jeden Kanal.
Einleitung:
Der ADC Pi Zero wird über den GPIO-Port des Raspberry Pi Zero mit Strom versorgt. Erweiterte Pins am GPIO-Anschluss ermöglichen es, den ADC Pi Zero zusammen mit anderen Erweiterungsplatinen zu stapeln.
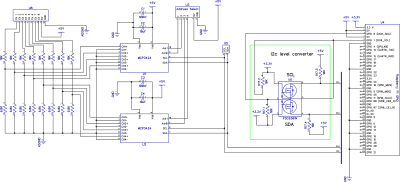
Die beiden MCP3424 A/D-Wandler kommunizieren über i2c mit dem Raspberry Pi, so dass Sie acht analoge Eingänge zur Verfügung haben. Ein Logik-Pegel-Wandler ist auf dem ADC Pi Zero Board enthalten und bietet einen gepufferten 5V i2c Port, der es einfach macht, andere I2C Geräte hinzuzufügen, die mit 5 Volt arbeiten, ohne den 3,3 Volt i2c Port des Raspberry Pi zu beschädigen. Der i2c-Puffer verwendet N-Kanal-Mosfets mit einem maximalen Drainstrom von 100mA.
Die I2C-Adressbits sind über die integrierten Jumper wählbar. Der MCP3424 unterstützt bis zu 8 verschiedene I2C-Adressen, so dass man mit zwei A/D-Wandlern auf jedem ADC Pi Zero bis zu 4 ADC Pi Zero Boards auf einem einzigen Raspberry Pi Zero stapeln kann, was 32 ADC-Eingänge ergibt.
Der MCP3424 enthält eine integrierte 2,048V-Referenzspannung mit einem Eingangsbereich von ±2,048V differentiell (Vollausschlag von 4,096V/PGA). Ein programmierbarer Verstärker bietet dem Benutzer eine wählbare Verstärkung von x1, x2, x4 oder x8, bevor die Analog-Digital-Wandlung stattfindet.
Die Datenrate für die Analog-Digital-Wandlung beträgt 3,75 (17 Bit), 15 (15 Bit), 60 (13 Bit) oder 240 (11 Bit) Samples pro Sekunde. Datenrate und Auflösung können in der Software über die I2C-Schnittstelle konfiguriert werden.
Wir haben einen Artikel in der Wissensdatenbank, ADC-Abtastratenvergleich mit detaillierteren Beispielinformationen und Testskripten zum Vergleich der verschiedenen Bit- und Abtastraten des MCP2424 ADC-Chips.
Nicht verwendete Eingänge sollten mit Masse verbunden werden.
Wenn Sie eine höhere Eingangsspannung abtasten möchten, können Sie unser ADC Pi Eingangsspannungs-Rechner um die zusätzlich benötigten Widerstände und Berechnungswerte zu finden.
Auswahl der I2C-Adresse
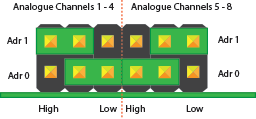
Der Analog-Digital-Wandler MCP3424 enthält zwei Adress-Select-Pins, die mit Vss, Vdd verbunden werden können oder potentialfrei bleiben. Dies ergibt 8 mögliche I2C-Adressen für jeden Chip. Der ADC Pi Zero enthält zwei MCP3424 Chips, so dass Sie bis zu 4 ADC Pi Zero Boards auf einem einzigen Raspberry Pi stapeln können. Um die Adressauswahl auf dem ADC Pi Zero zu vereinfachen, haben wir eine Reihe von Adressauswahl-Pins vorgesehen, die mit den mitgelieferten Jumpern konfiguriert werden können. Die Abbildungen unten zeigen die vier empfohlenen Konfigurationen für Ihren ADC Pi Zero und die dazugehörigen I2C-Adressen.
Anmerkung:
Trennen Sie den ADC Pi Zero vom Raspberry Pi, bevor Sie die Adresspins ändern. Möglicherweise müssen Sie die 5V und Masse mit einem Widerstand kurzschließen, um die Kondensatoren zu entladen, damit die neuen Adressen erkannt werden.
I 2 C Adresstabelle
| Adr 0 |
Adr 1 |
I2C-Adresse |
| Niedrig oder schwimmend |
Niedrig oder schwimmend |
0x68 |
| Niedrig |
Schwimmer |
0x69 |
| Niedrig |
Hoch |
0x6A |
| Schwimmer |
Niedrig |
0x6B |
| Hoch |
Niedrig |
0x6C |
| Hoch |
Schwimmer |
0x6D |
| Hoch |
Hoch |
0x6E |
| Schwimmer |
Hoch |
0x6F |
Warnung
Verbinden Sie unter keinen Umständen die beiden mittleren Pins miteinander. Dadurch entsteht ein direkter Kurzschluss zwischen den 5V- und den Erdungspins und Ihr Raspberry Pi und ADC Pi Zero Board werden beschädigt oder zerstört.

Empfohlene Adresskonfigurationen
Konfiguration 1:
Analoge Kanäle 1-4 = I2C Adresse: 0x68
Analoge Kanäle 5-8 = I2C Adresse: 0x69
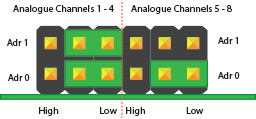
Konfiguration 2:
Analoge Kanäle 1-4 = I2C Adresse: 0x6A
Analoge Kanäle 5-8 = I2C Adresse: 0x6B
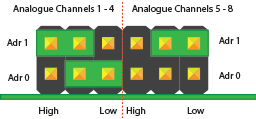
Konfiguration 3:
Analoge Kanäle 1-4 = I2C Adresse: 0x6C
Analogkanäle 5-8 = I2C Adresse: 0x6D
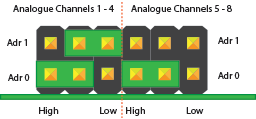
Konfiguration 4:
Analoge Kanäle 1-4 = I2C Adresse: 0x6E
Analogkanäle 5-8 = I2C Adresse: 0x6F
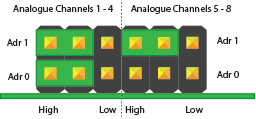
Datenblätter
MCP3424
Kompatibilitäts-Tabelle
| Raspberry Pi Model A |
Nein |
| Raspberry Pi Model B |
Nein |
| Raspberry Pi 1 Model A+ |
Ja |
| Raspberry Pi 1 Model B+ |
Ja |
| Raspberry Pi 2 Model B |
Ja |
| Raspberry Pi 3 Model B |
Ja |
| Raspberry Pi Zero |
Ja |
| ODroid C1 |
Ja |
| ODroid C2 |
Ja |